Have you just bought a CBD product and you want to know how it works? Have you read that CBD mainly interacts with the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 but you don’t know what they are?
Don’t worry, we’ll explain it to you!
CB1 and CB2 receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system, a cellular signalling system present in all mammals that plays an important role in maintaining balance in the body.
Specifically, CB1 receptors are found predominantly in the central nervous system, brain and spinal cord, and they are involved in the modulation of pain, mood, memory, appetite, and sensory perception. They are the main receptors responsible for the psychoactive effects of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), which is the cannabinoid found in cannabis.
On the other hand, CB2 receptors are mainly present in the immune system and peripheral tissues, such as the spleen, colon, pancreas and immune cells. Their functions include the regulation of the immune response, inflammation and pain. They interact mainly with cannabinoids such as CBD (cannabidiol) and CBC (cannabicromene), contributing to anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects without causing psychoactive effects.
In this article, we want to focus on the CB1 receptor, given its significant impact on the functioning of the nervous system and its direct influence on multiple essential bodily processes.
CB1: what are they and where are they found?
CB1 receptor, or cannabinoid receptor 1, is one of the main receptors of the endocannabinoid system, widely distributed in our bodies, which started to gain much interest in the 90s.
They are found in many parts of our body, with the highest concentration in the nervous system, but are also present in other tissues and organs. Here is a list of the main areas where CB1 receptors are found:
- Brain: especially in the areas related to memory, motor control, appetite, emotions and pain perception (e.g. hippocampus, cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, cerebellum);
- Spinal cord: they are involved in the modulation of pain and sensory response;
- Peripheral nerves: they affect pain transmission and motor control;
- Eyes: they are also found in the retina and may affect vision;
- Respiratory system: in the airways, where they may affect breathing;
- Reproductive system: in organs such as testicles, ovaries and uterus, affecting fertility and other reproductive functions;
- Heart and cardiovascular system: involved in the regulation of blood pressure and heart rate;
- Liver: they may affect metabolism and energy balance;
- Gastrointestinal system: they modulate intestinal motility, appetite and digestion;
- Adipose tissues: they influence the regulation of fat metabolism and energy storage;
- Skin: they are found in cutaneous nerves and contribute to the modulation of the sensation of pain and itching.
Their distribution in several areas of the body explains why cannabinoids may influence multiple functions, varying the effects according to the area where CB1 receptors are activated.
CB1 receptor structure
CB1 receptors (type 1 cannabinoid receptors) belong to the family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Their structure is similar to that of many other receptors in this family, characterised by seven transmembrane domains that cross the cell membrane.
Let’s take a look at the structure of the CB1 receptor:
- Seven transmembrane helices: These helical domains cross the cell membrane seven times, forming a kind of tunnel within the membrane. This structure allows the receptor to transmit signals from outside to inside the cell.
- Extracellular domain: The N-terminal end of the receptor is located outside the cell. This is where ligands such as cannabinoids (e.g. THC or endocannabinoids such as anandamide) bind, activating the receptor.
- Intracellular domain: The C-terminal end is inside the cell and is responsible for activating G-proteins. These G proteins are crucial for transmitting the signal within the cell and activating subsequent biochemical processes.
- Coupled G proteins: When a cannabinoid binds to the CB1 receptor, this activates G proteins within the cell. G-proteins then influence intracellular second messengers, such as adenylate cyclase, changing the behaviour of the cell.
The three-dimensional structure of CB1, discovered through techniques such as X-ray crystallography, revealed that the receptor is dynamic, changing shape when a ligand binds, which helps explain its ability to bind to different types of molecules with different effects.
CB1 receptors: what is their function?
CB1 receptors are responsible for receiving and mediating the effects of specific substances found in hemp, such as:
- Pain regulation: CB1 receptors play an important role in modulating pain perception, acting as a mediator in inhibiting the transmission of pain signals in the central nervous system. This helps reduce pain sensitivity, making it an important target for the treatment of chronic and neuropathic pain, such as in arthritis, nerve injury and other painful conditions.
- Appetite and metabolism control: CB1 receptors are closely involved in regulating appetite and energy balance. When activated, they stimulate the sensation of hunger, increasing food intake. They also influence lipid and glucose metabolism, playing an important role in managing body weight and energy metabolism.
- Management of mood and emotions: CB1 contributes to the regulation of mood, stress and emotions. Its activation is related to anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, as it influences the secretion of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, involved in the regulation of emotional well-being. This receptor is also related to the body’s ability to handle stress, providing a support mechanism for mental equilibrium.
- Modulation of memory and learning: CB1 receptors are located in areas of the brain such as the hippocampus, which are essential for memory and learning. Their activation can modulate cognitive processes, influencing memory formation and recall.
- Neurological protection: CB1 receptors have significant neuroprotective properties, helping to reduce inflammation in the brain and protecting neurons from damage caused by injury, oxidative stress or neurodegenerative diseases. This protection may be helpful in preventing or mitigating conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological diseases.
- Motor regulation: The CB1 receptor is involved in the control of movement and coordination through its interaction with the central motor system. This is particularly relevant in conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and other motor dysfunctions, where proper modulation of movement may be impaired.
- Control of gastrointestinal functions: CB1 has a significant impact on intestinal motility, influencing the contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscles of the digestive tract. In addition, it may help regulate nausea and vomiting, making it useful in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.
Knowing how CB1 receptors work and where they are located is crucial to fully understanding the influence of cannabinoids on our health and overall well-being.
CB1 and G-proteins: how do they interact?
When cannabinoids, such as THC or natural endocannabinoids, bind to CB1 receptors, these activate specific G-proteins within the cell.
G-proteins are crucial as they modulate various intracellular second messengers, such as adenylate cyclase, which is inhibited, and facilitate the opening of ion channels, such as potassium channels, helping to regulate cellular activity.
This complex mechanism reduces the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate and dopamine, modulating neuronal activity and affecting a wide range of functions, including pain control, mood regulation, appetite and memory.
In short, G-proteins act as essential intermediaries between the CB1 receptor and the cellular response, making a modulated and specific response to cannabinoids possible.
CBD and endocannabinoid system
CBD, or cannabidiol, is one of the main cannabinoids found in hemp plants. Unlike THC, CBD has no psychoactive effects but interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ESA), regulating numerous physiological processes, such as pain, mood, appetite and sleep.
CBD does not bind directly to CB1 receptors but modulates their activity. It acts as a negative allosteric modulator, altering the shape of CB1 receptor and reducing its affinity for other molecules such as THC. This explains why CBD can mitigate some psychoactive effects of THC, making it less invasive to the body.
When cannabinoids bind to CB1 receptors, these activate G-proteins that, as mentioned earlier, reduce the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate and dopamine, modulating crucial functions such as pain control, mood and memory.
CBD, even though it doesn’t bind directly to the CB1 receptor, it manages to influence these processes indirectly, contributing to treating conditions such as anxiety, chronic pain, and neurological disorders.
Its ability to interact with the endocannabinoid system makes it a promising option for alternative treatments, with less side effects than conventional drugs, opening up new possibilities in health and well-being management.
What is the right CBD product for me?
After learning about the benefits of CBD for our body, you may be wondering which CBD product is best suited to your needs.
There are many ways of taking CBD, each suited to individual needs and preferences. Let’s see together which one is right for you.
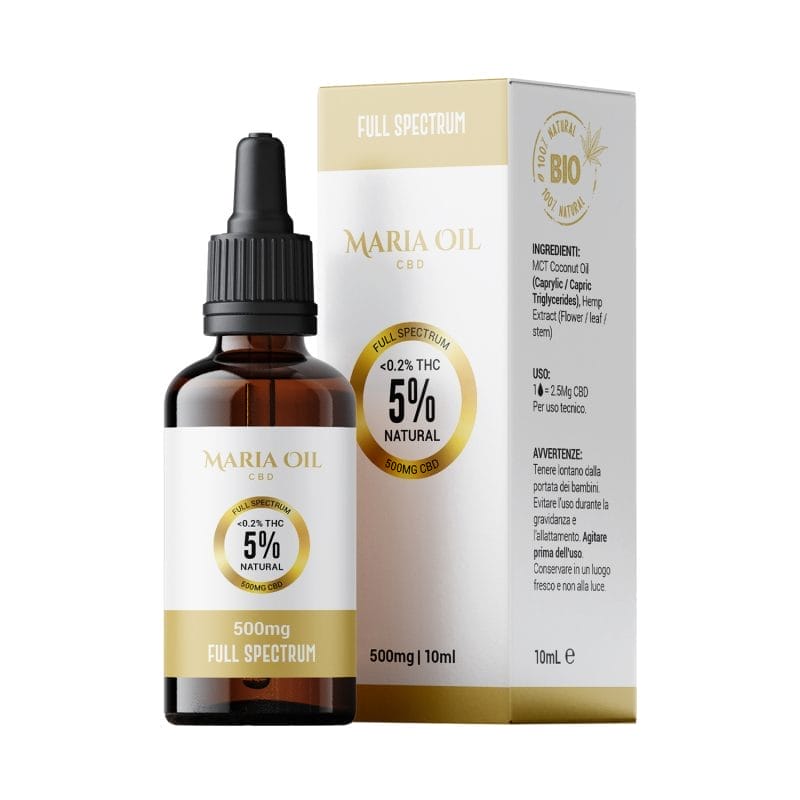
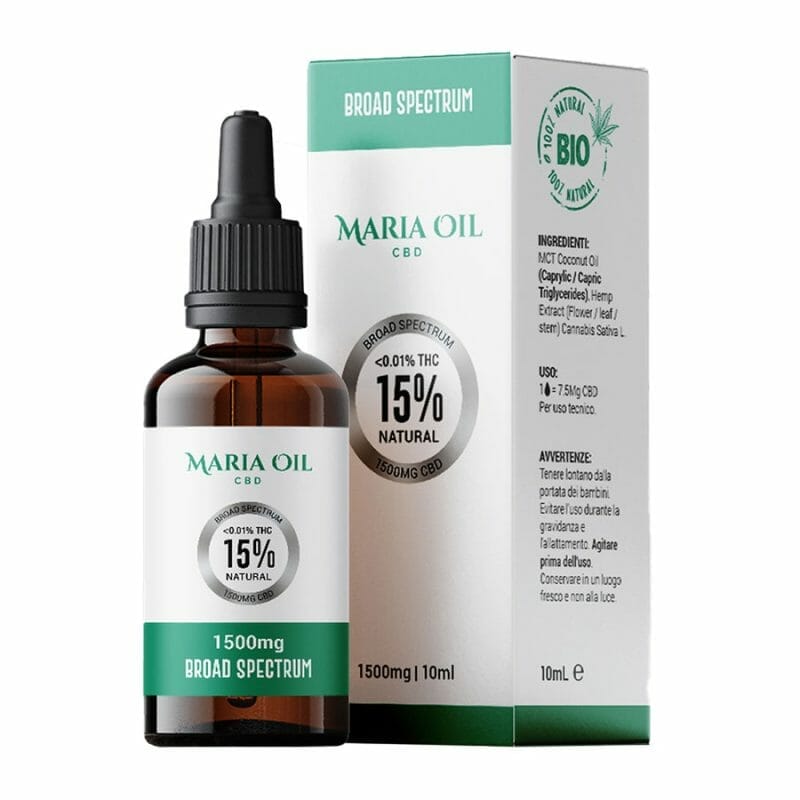
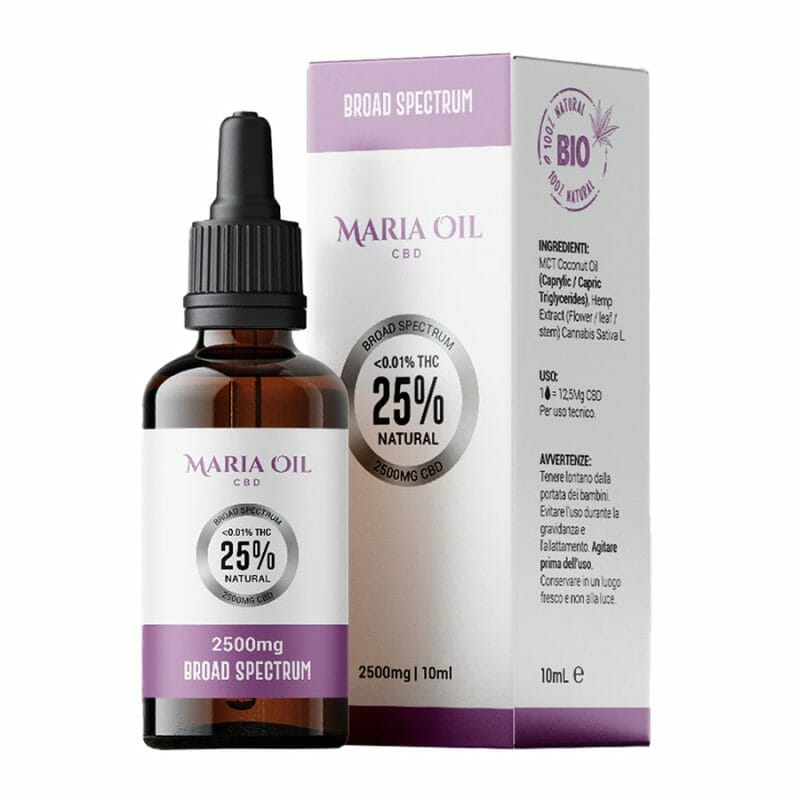
CBD oil is definitely one of the most popular products in this field, which can be administered under the tongue for rapid absorption, spread directly on the affected area or added to food and drink.
Consumers find it very useful mainly for:
- Reducing anxiety, stress and depression
- Improve the quality of sleep
- Managing chronic pain or inflammation
- Improving concentration and mental clarity
- When experiencing a drop in energy or moodiness
Oils can have different concentrations of CBD, to be chosen according to the intensity and severity of the symptoms.
For low intensity, you can resort to 5% or 10% CBD oil:
For medium to high intensity, 15% or 20%CBD oil:
Finally, for very high intensity, 25% or 30% CBD oil is definitely for you:
An alternative to oil could be CBD capsules, which are very convenient for their ease of use and the possibility of having precise dosages to take at any time.
-
 Capsule CBD 25mg£29.90
Capsule CBD 25mg£29.90 -
 CBD Capsules 15mg (450mg)£19.90
CBD Capsules 15mg (450mg)£19.90
For more specific treatments focusing on specific areas of the body, Maria CBD Oil has developed a line of cosmetics for every need:
-
 CBD Eye Cream£11.00
CBD Eye Cream£11.00 -
 CBD Moisturising Face Cream£27.00
CBD Moisturising Face Cream£27.00 -
 Hemp Chapstick£6.99
Hemp Chapstick£6.99
If, on the other hand, a more complete experience in every respect is desired, there are variations of weed or legal hashish with unique and tasty flavours, without the risk of altering the mind.
-
 Afghan£8.50 – £249.00From 2,49 €/gr
Afghan£8.50 – £249.00From 2,49 €/gr -
 Amnesia Haze£3.50 – £350.00From 0,88 €/gr
Amnesia Haze£3.50 – £350.00From 0,88 €/gr -
 IceRock | Legal Hashish£8.00 – £255.00From 2,55 €/gr
IceRock | Legal Hashish£8.00 – £255.00From 2,55 €/gr -
 Lemon Haze£3.50 – £270.00From 0,88 €/gr
Lemon Haze£3.50 – £270.00From 0,88 €/gr -
 MoonRock | Legal Hashish£8.50 – £249.00From 2,49 €/gr
MoonRock | Legal Hashish£8.50 – £249.00From 2,49 €/gr -
 Red Lebanese | Legal Hashish£8.50 – £249.00From 2,49 €/gr
Red Lebanese | Legal Hashish£8.50 – £249.00From 2,49 €/gr
Finally, a very popular method among smokers is CBD Vaping or using CBD Vape Pens, i.e. electronic cigarettes that offer a quick and extremely convenient experience.
-
 Banana Smoothie | CBD Vape Pen£19.00
Banana Smoothie | CBD Vape Pen£19.00 -
 Battery 1 ml POD£29.00
Battery 1 ml POD£29.00 -
 Cherry Pie | CBD Vape Pen£19.00
Cherry Pie | CBD Vape Pen£19.00 -
 Orange Pod | CBD Vapes£11.00
Orange Pod | CBD Vapes£11.00 -
 Strawberry Pod | CBD Vapes£11.00
Strawberry Pod | CBD Vapes£11.00
Conclusion
In short, there are many solutions for those who want to enjoy the benefits of CBD.
CB1 receptors play a key role in the interaction between our body and CBD, modulating vital functions such as mood, pain control, and appetite. Thanks to this connection, CBD products offer a wide range of benefits, making them suitable for many personal needs. The options available are countless and range from oils to topicals, capsules to edibles, providing solutions for every preference.
Visit our Maria CBD Oil shop to discover the full range of CBD products designed to meet your every wellness need.
 Contact us
Contact us